For more than a century, stitches have been the standard method for closing wounds after injuries and surgeries. Whether it’s a minor cut or a complex operation, sutures and staples have played a vital role in protecting wounds from infection and supporting the healing process. But while they’re effective, they often come with a set of problems—pain, prolonged healing times, infection risks, and, of course, scars. Patients dread the discomfort of stitches and the telltale marks they leave behind.
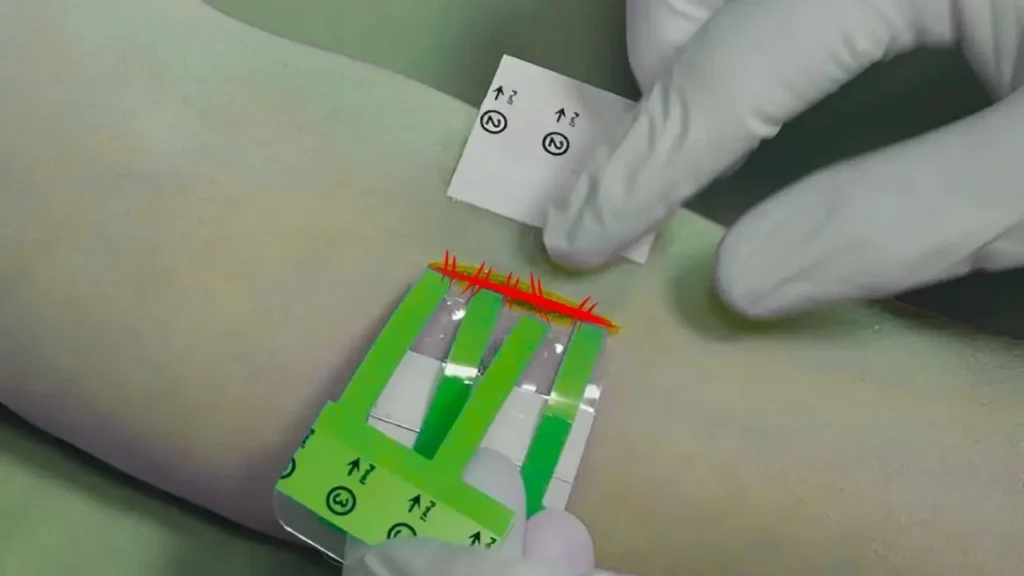

Now, a new breakthrough in wound closure technology is making headlines in the medical world. Scientists have developed a revolutionary method that can seal cuts in seconds without the need for stitches or staples. More importantly, this technique promises minimal to no scarring. It represents a major step forward in how we treat wounds—making healing faster, safer, and cosmetically better.
New Wound Closure Seals Cuts in Seconds Without Scars
The phrase “goodbye to stitches” is becoming more than just a hopeful expression. It reflects a real technological leap in how wounds can be treated. A team of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has created a special light-activated adhesive that can bond tissues together in just 30 seconds. Unlike sutures, this adhesive doesn’t require puncturing the skin with needles. Instead, it forms a secure seal over the wound, drastically reducing trauma and the chances of infection.
This new technique isn’t just about speed; it’s also about quality. Traditional stitches often create tension at the wound site, which leads to visible scars. This adhesive technology eliminates that tension, allowing the skin to heal more smoothly. Early trials have already shown that this method can lead to better functional and cosmetic results. Patients can expect faster recovery times, less pain, and minimal visible scarring.
Overview Table
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Light-activated biopolymer | A flexible, biocompatible material that seals wounds when exposed to a special blue light. | Rapid, secure wound closure without stitches. |
| Wet-tissue adhesion | Designed to work even on moist tissue, making it ideal for complex internal procedures. | Reliable closure in challenging surgical environments. |
| Degradable and non-traumatic | Biodegradable material that eliminates the need for needle penetration. | Reduced tissue damage and faster healing. |
| Clinical progress | Already authorized by regulatory bodies for nerve repair applications. | On the path to real-world use. |
| Scar-reduction potential | No puncture wounds or tension at wound edges. | Minimal to no scarring. |
How the New Technology Works
The innovation behind this adhesive is simple yet brilliant. It involves a soft, flexible polymer that can be applied directly onto the wound site. Once in place, surgeons activate the adhesive with a brief burst of blue light. This triggers a chemical reaction that makes the polymer bond tightly to the surrounding tissue, creating a watertight and airtight seal.
Unlike stitches or staples, which can irritate and damage tissue, this technique doesn’t involve puncturing the skin. That means less trauma to the wound and surrounding area. The adhesive is also biocompatible, meaning it integrates naturally with the body and eventually degrades safely over time. This eliminates the need for removal procedures and reduces the risk of complications.
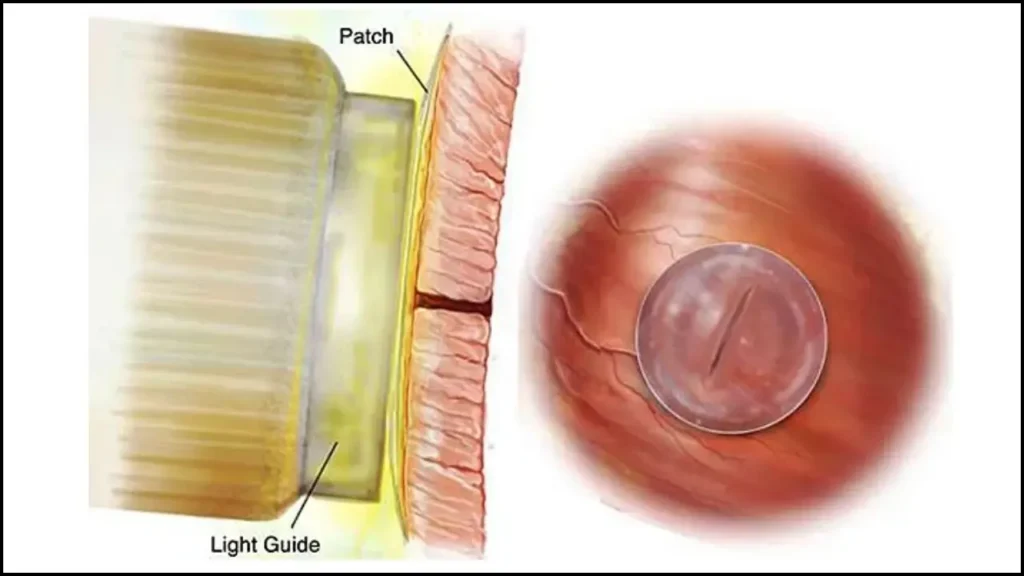
What makes this technology even more impressive is its ability to work in wet environments—something that has been a major challenge in surgery. Traditional adhesives often fail when moisture is present. But this polymer is specifically designed to adhere strongly to wet tissue, making it ideal for both external and internal surgical applications.
Why This Matters
The way we close wounds has a direct impact on how well they heal and how they look afterward. Stitches and staples can be effective, but they have clear limitations. They can leave visible marks, require time-consuming procedures, and sometimes increase the risk of infection. They can also be uncomfortable for patients, especially when they have to be removed later.
This new wound closure method changes all that. By creating a strong seal without puncturing the skin, the adhesive reduces pain, accelerates healing, and minimizes scarring. Surgeons can close wounds faster, and patients can recover more comfortably. For people undergoing procedures on visible areas like the face or hands, this can make a huge difference in how they feel about their appearance after healing.
Real-World Applications
The technology is already being used in clinical trials for nerve repair, with excellent results. All patients in these early studies recovered both motor and sensory function fully. This success is paving the way for broader applications. Surgeons are exploring how the adhesive can be used in other areas, including:
- Hernia repair: to close incisions securely without the complications of sutures.
- Cardiovascular surgery: where wet environments make traditional closures difficult.
- Emergency medicine: for rapid wound sealing in trauma situations.
- Cosmetic and reconstructive surgery: where scar-free healing is especially important.
Because the material is biodegradable, it doesn’t have to be removed after healing is complete. This makes it a particularly appealing option in procedures where follow-up surgeries would otherwise be required to remove sutures or staples.
Challenges and Considerations
As promising as this technology is, there are still hurdles to overcome before it can completely replace stitches in all cases.
- Cost and accessibility: New technologies often come with higher initial costs. Hospitals and clinics will need to balance these costs with the long-term benefits.
- Training: Surgeons will need to learn new techniques to use the adhesive effectively. Integration into existing surgical workflows will take time.
- Regulatory approval: While nerve repair applications have received authorization, other uses will require more trials and testing.
- Wound complexity: For very large or deep wounds, stitches might still be required alongside or instead of adhesive.
- Long-term studies: More data is needed on how well this adhesive performs over years, not just months.
Looking Toward the Future
Imagine walking out of surgery without the discomfort of stitches. No itchy healing process. No visible scars. That’s the future this innovation is promising. If widely adopted, this light-activated adhesive could transform surgical care worldwide.
The potential impact goes beyond cosmetics. Faster wound closure and reduced trauma mean lower infection rates, less need for follow-up visits, and quicker returns to normal life. It could also reduce costs over time by shortening operating times and hospital stays.
Patient Benefits at a Glance
- Faster healing: No need for suture removal or extended recovery periods.
- Less pain: No needle punctures or pulling at the skin.
- Minimal scarring: A smooth finish that heals naturally.
- Lower infection risk: A clean seal reduces exposure to bacteria.
- Broader use: From small cuts to complex surgeries.
FAQs About New Wound Closure Seals Cuts in Seconds Without Scars
1. How is this adhesive different from medical glue currently available?
2. Is the adhesive safe for all types of wounds?
3. Will this replace stitches completely?
4. How long does it take to apply the adhesive?
5. Is it more expensive than traditional stitches?
Conclusion
The development of this light-activated, biodegradable adhesive is a true game-changer in modern medicine. By eliminating the need for stitches in many cases, it offers patients a faster, less painful, and nearly scar-free way to heal. While traditional sutures may not disappear overnight, this innovation represents a major step toward a future where wound care is cleaner, quicker, and more comfortable.
Saying “goodbye to stitches” is no longer just a catchy phrase—it’s the reality of a new era in surgical healing. As the technology continues to advance and gain approval for more applications, it has the potential to redefine how wounds are treated worldwide, improving both medical outcomes and patients’ quality of life.